
BSC is a System Bringing Your Business Strategy to Life
The systematic process of the implementation of the company's strategy involves the use of the maximum possible instrumental apparatus, scientifically and practically grounded, through which the outlined long-term goals will become obvious facts. One such tool is the Balanced Scorecard (BSC).
The BSC model is the result of the fundamental research “Organization of the Future Performance” led by David P.Norton and Robert S.Kaplan.
One of the factors that predetermined the need for the creation of BSC was the awareness of that a focus solely on financial performance cannot serve as a full-fledged basis for strategic management.
BSC, based on the principle of "cause-effect", is a multifunctional performance assessment system that includes financial and non-financial indicators, reflects the trajectory of the company's strategy and helps to implement the strategy. BSC synthesizes in itself objective easily quantifiable indicators and results, and subjective, reflecting the parameters of future growth.
Four perspectives are highlighted within the BSC (Figure 1).
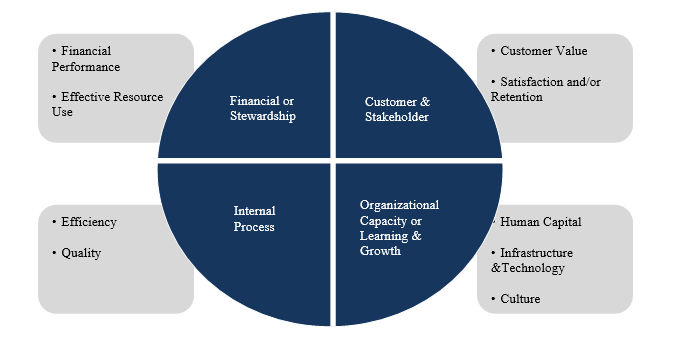
Figure 1 – BSC perspectives
The Financial perspective focuses on financial performance and financial resource efficiency, and may include the following objectives:
-
increase profitability;
-
growth sales;
-
cost reduction, cost leadership;
-
increase cash flow, business value, etc.
Customer & Stakeholder projection views the company from the perspective of customers and stakeholders. Indicators of this perspective can include such as market share, retention and expansion of the customer base, customer satisfaction and loyalty, image, reputation, relationships with stakeholders and customers, etc., and this requires an understanding of their requests and needs.
The Internal process perspective reflects the activities that are key to achieving the goals of all stakeholders, and the indicators are productivity, cycle time, costs, lead times, product quality, etc.
The Organizational Capacity or Learning & Growth perspective reflects targets and metrics related to human capital, infrastructure, technology, culture, which are key to achieving outstanding results. The strategic goals of this perspective are the fundamental factors in the implementation of the goals and objectives set by the three previous components.
One of the powerful elements of BSC is strategic mapping, which reflects information about how the company creates value.
The BSC strategy map is a model showing how the strategy integrates intangible assets and value creation processes (Figure 2).
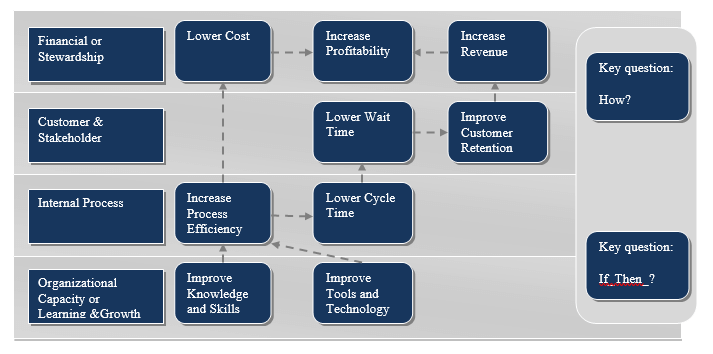
Figure 2 – BSC strategic map model
Firstly, value creation is mediated. The impact of improving intangible assets on financial results is carried out through causal relationships, for example, training company employees within the framework of TQM concepts has a direct impact on improving quality, which contributes to customer satisfaction and increased loyalty, which in turn has an effect on increasing sales and profitability.
Secondly, value is contextual, i.e. the value of intangible assets depends on their relevance to the company's strategy.
Thirdly, the value is of a potential nature - internal processes, among which one can single out, for example, design, production, delivery are necessary for the transformation of the potential value of intangible assets into tangible value.
Fourthly, the interconnectedness of assets, i.e. the value of intangible assets arises only when they are effectively combined with other tangible and intangible assets and resources.
The goals of all four perspectives are interrelated cause and effect relationships. The causal nature linking the four BSC perspectives is the foundation upon which the strategic map is built.
***
Thus, BSC has the ability to systematically assess, adjust, and integrate within the four strategic perspectives different, universal, as well as unique for each company indicators and elements, forms and develops, firstly, a multidimensional vision of the subjects of strategic management, and secondly, a full-fledged vision of the company, allowing to consider the trajectory of business development through the prism of financial and non-financial components.